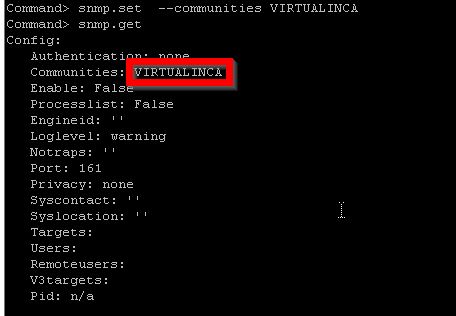
To enable the vCenter Server and ESXi SNMP agent to send and receive SNMP v1 and v2c messages, you must configure at least one community for the agent.
vCenter Appliance
1. Access the appliance shell and log in as a user who has the administrator or super administrator role. The default user with a super administrator role is root.
Command> snmp.get
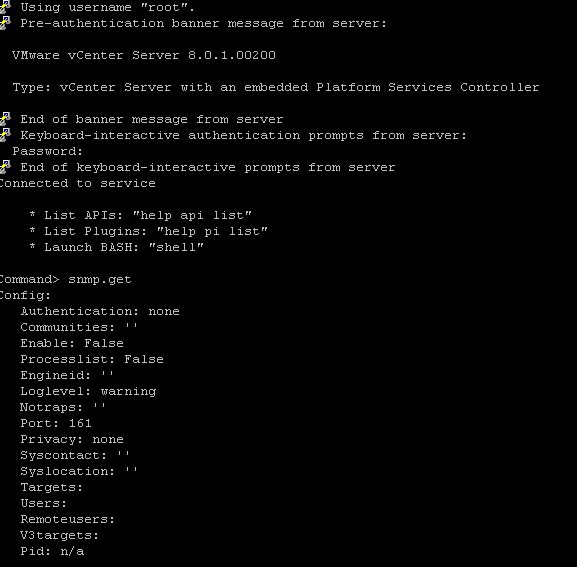
Command> snmp.set --communities VIRTUALINCA
snmp.set --targets target_address@port/community
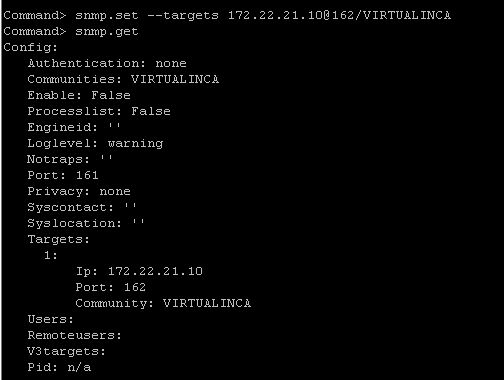
Here target_address, port, and community are the address of the target system, the port number to send the notifications to, and the community name, respectively. The port value is optional. If you do not specify a port, the default port,161, is used.
Each time you specify a target with this command, the settings you specify overwrite all previously specified settings. To specify multiple targets, separate them with a comma.
Command> snmp.set --loglevel warning
Command> snmp.enable
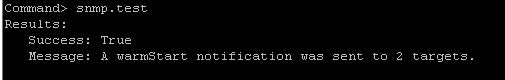
To send a test trap to verify that the agent is configured correctly, run the following command:
ESXi
To enable the ESXi SNMP agent to send and receive SNMP v1 and v2c messages, you must configure at least one community for the agent. If you run ESXCLI commands through ESXCLI, you must supply connection options that specify the target host and login credentials. If you use ESXCLI commands directly on a host using the ESXi Shell, you can use the commands as given without specifying connection options. For more information on connection options see ESXCLI Concepts and Examples.
1. Access the shell through SSH and log in as a root.
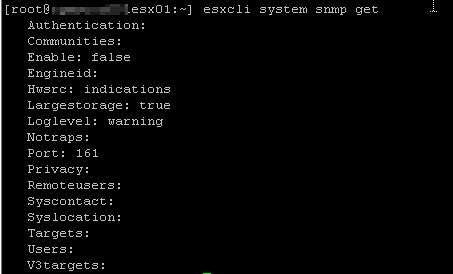
2. Run the following command to check the current settings
[root@esx01:~] esxcli system snmp get
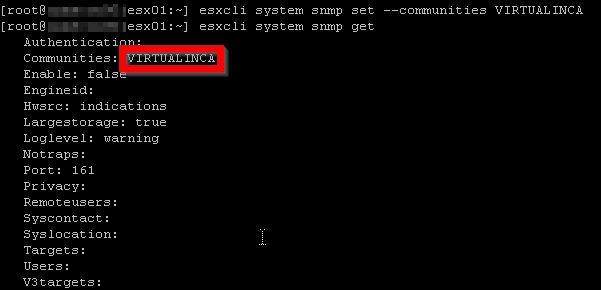
3. Run the following command with the –communities option to configure an SNMP community
[root@esx01:~] esxcli system snmp set --communities VIRTUALINCA
4. To send SNMP v2c notifications with the SNMP agent, you must configure the target, that is the receiver, unicast address, community, and an optional port. If you do not specify a port, the SNMP agent sends notifications to UDP port 162 on the target management system by default. Run the following command:
[root@esx01:~] esxcli system snmp set --targets target_address@port/community
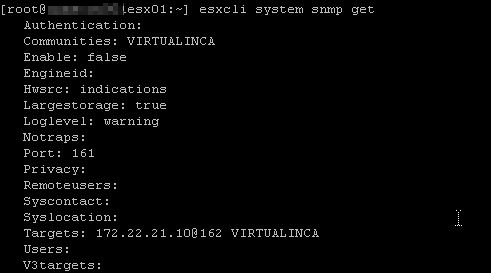
Here target_address, port, and community are the address of the target system, the port number to send the notifications to, and the community name, respectively. The port value is optional. If you do not specify a port, the default port,161, is used.
Each time you specify a target with this command, the settings you specify overwrite all previously specified settings. To specify multiple targets, separate them with a comma.
5. You can configure the loglevel with the following command:
[root@esx01:~] esxcli system snmp set --loglevel warning
[root@esx01:~] esxcli system snmp set --enable true
To send a test trap to verify that the agent is configured correctly, run the following command:
[root@esx01:~] esxcli system snmp test